How to Treat Infected Bite: Your Essential Guide to Healing

A bite, whether from a playful pet, a buzzing insect, or an unexpected encounter, can quickly turn from a minor annoyance into a serious concern if it becomes infected. Understanding how to treat an infected bite is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a swift recovery. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to identify, manage, and heal infected bites, bringing you peace of mind and a path back to comfort.
Understanding the Dangers of an Infected Bite
The festive spirit of the holidays often involves increased outdoor activities, social gatherings, and closer interactions with pets. While these moments are joyous, they also present opportunities for bites. A simple scratch or nip can harbor bacteria, and if left untreated, these microscopic invaders can trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses, leading to a painful and potentially dangerous infection. Recognizing the signs of an infected bite is the first, and perhaps most critical, step in effective treatment. Ignoring an infected bite can lead to severe consequences, including sepsis, tissue damage, and even permanent health issues. Therefore, arming yourself with the knowledge of how to treat an infected bite is an essential part of responsible self-care.
What Constitutes an Infected Bite?
An infected bite occurs when bacteria or other pathogens enter the skin through a break in the skin caused by the bite. The body’s immune system attempts to fight off these invaders, but if the infection takes hold, it can spread, causing a range of symptoms. It’s important to distinguish between a simple bite and one that shows signs of infection.
Common Culprits: What Bites Can Become Infected?
Many types of bites can lead to infection, depending on the source and the environment.
Animal Bites
- Mammalian Bites: Dogs, cats, and other mammals can carry a variety of bacteria in their mouths, including Pasteurella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus. These bacteria are particularly adept at causing deep tissue infections.
- Rodent Bites: Bites from rats and mice can transmit diseases like rat-bite fever.
- Reptile Bites: Snake and lizard bites can introduce bacteria into the bloodstream, and venomous bites carry their own set of immediate dangers.
Insect Bites
- Mosquito Bites: While often itchy, mosquito bites can become infected if scratched excessively, introducing bacteria from the skin’s surface.
- Tick Bites: Tick bites are a significant concern due to the potential transmission of serious diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Even without a specific disease, the bite site can become infected.
- Spider Bites: Certain spider bites, particularly those from venomous species like the brown recluse or black widow, can lead to necrotic lesions and secondary infections.
- Bee and Wasp Stings: While primarily causing allergic reactions, the puncture wound from a sting can also become infected.
Human Bites
Human bites are often considered the most dangerous due to the high concentration of bacteria in the human mouth, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and E. coli.
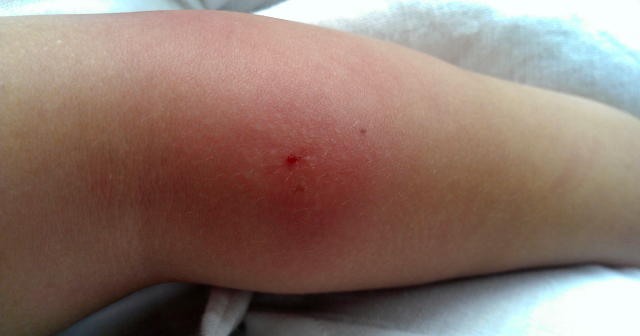
Recognizing the Red Flags: Signs of an Infected Bite
Early detection is key when it comes to how to treat an infected bite. The signs of infection can develop within hours or days of the initial bite. Look out for the following:
- Increased Redness and Swelling: The area around the bite will become noticeably redder and more swollen than a typical bite. This redness may spread outwards from the bite site.
- Warmth: The infected area will feel warm to the touch, indicating inflammation and increased blood flow to fight the infection.
- Pain and Tenderness: The bite will become increasingly painful and sensitive to touch. The pain may be throbbing or constant.
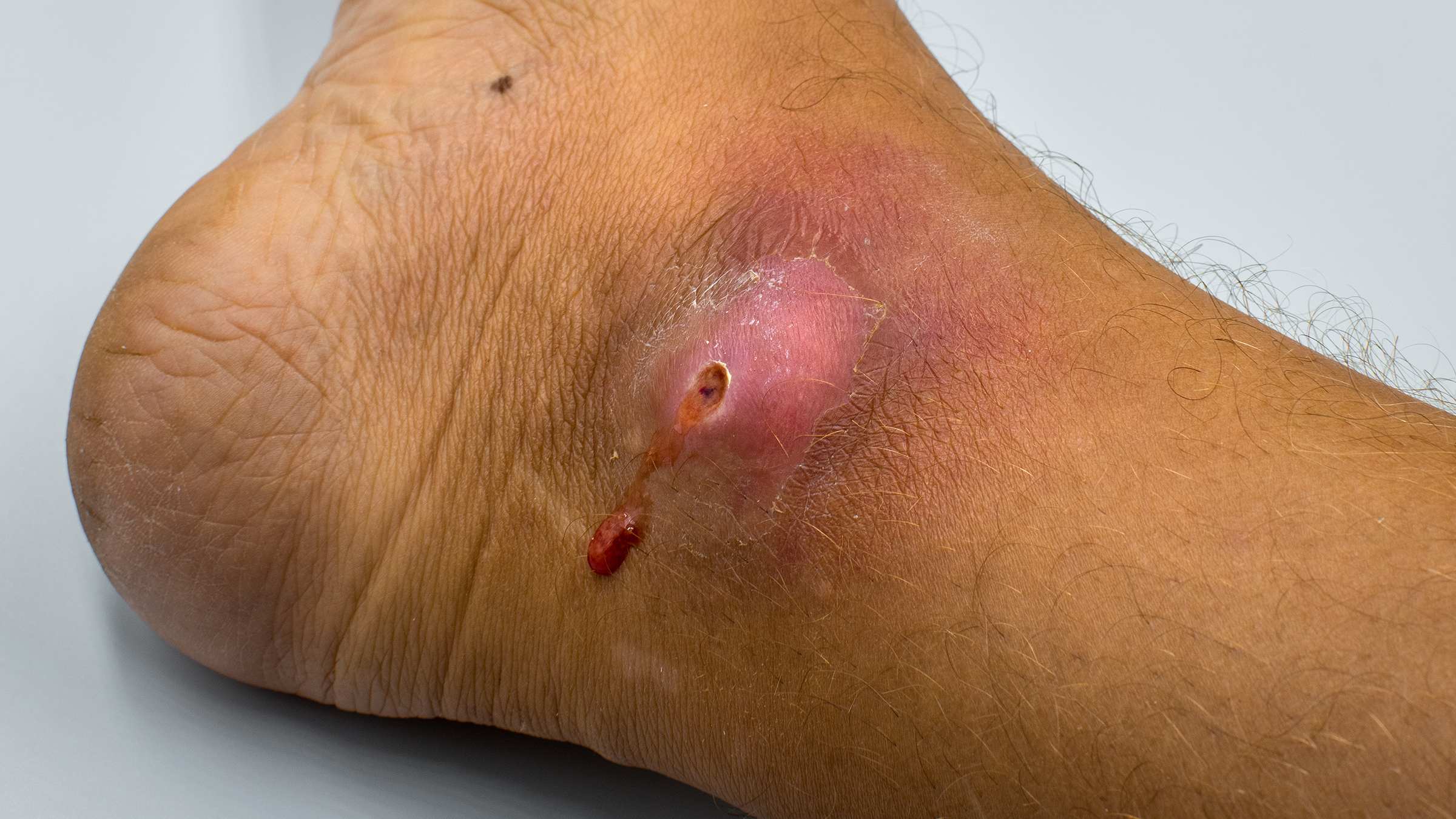
- Pus or Discharge: The presence of pus, a thick, yellowish or greenish fluid, is a clear sign of infection. This discharge may ooze from the bite wound.
- Fever and Chills: If the infection is spreading systemically, you may develop a fever, feel generally unwell, and experience chills.
- Red Streaks: Red streaks extending from the bite site up the limb can indicate lymphangitis, an inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, which is a serious sign of spreading infection.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: The lymph nodes closest to the bite area may become enlarged and tender as they work to filter out the infection.
- Delayed Healing: The bite wound may fail to heal or may even worsen over time.
Taking Charge: How to Treat an Infected Bite Effectively
Once you suspect an infected bite, prompt and appropriate action is essential. The approach to how to treat an infected bite will vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of bite.
Immediate First Aid: Your First Line of Defense
Even before you confirm an infection, proper first aid can significantly reduce the risk.
- Clean the Wound Thoroughly: Gently wash the bite area with mild soap and clean water. This helps remove any surface bacteria. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can further damage the skin.
- Apply Antiseptic: After cleaning, apply an over-the-counter antiseptic solution or ointment, such as hydrogen peroxide or an antibiotic ointment.
- Cover the Wound: Use a clean bandage to protect the bite from further contamination. Change the bandage regularly, especially if it becomes wet or dirty.
- Elevate the Affected Area: If the bite is on a limb, elevate it to help reduce swelling.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help: Crucial Steps for Serious Infections
While home care can be effective for minor bites, certain situations demand immediate medical attention. How to treat an infected bite effectively often involves professional intervention.
- Deep or Puncture Wounds: Bites that break the skin deeply, especially puncture wounds, are at higher risk of infection and may require medical evaluation.
- Signs of Spreading Infection: If you notice red streaks, fever, chills, or significant swelling and pain, seek medical help immediately.
- Animal Bites from Unknown Sources: Bites from stray animals or animals exhibiting unusual behavior should always be evaluated by a doctor.
- Bites on Sensitive Areas: Bites on the face, hands, feet, or near joints require careful monitoring and professional assessment.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems (due to conditions like diabetes, HIV, or chemotherapy) are more susceptible to severe infections and should consult a doctor for any bite.
- Suspected Rabies Exposure: If there’s any possibility of rabies exposure, immediate medical attention is critical.
Medical Treatments for Infected Bites: A Doctor’s Expertise
A healthcare professional will assess the bite and the signs of infection to determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Antibiotics: The Cornerstone of Infection Treatment
- Oral Antibiotics: For most bacterial infections, a course of oral antibiotics will be prescribed. The type of antibiotic will depend on the suspected bacteria. It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
- Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics: In severe cases where the infection is widespread or not responding to oral medication, IV antibiotics may be administered in a hospital setting.
Wound Care and Drainage
- Debridement: If there is dead or damaged tissue, a doctor may need to debride (remove) it to promote healing and prevent further infection.
- Incision and Drainage (I&D): If an abscess (a collection of pus) has formed, a doctor may need to make a small incision to drain the pus and clean the area.
Tetanus Shot Update
- Tetanus Prophylaxis: If your tetanus vaccination is not up-to-date, your doctor may recommend a tetanus booster shot, as puncture wounds are a common entry point for tetanus bacteria.
Antiviral Medications
- Rabies Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP): If there’s a risk of rabies, a series of rabies vaccines and immunoglobulin injections will be administered. This is a critical intervention and requires immediate medical attention.
Home Care Strategies to Support Healing
While medical treatment is paramount for infected bites, supportive home care can significantly aid in the healing process.
Keeping the Wound Clean and Dry
- Regular Cleaning: Continue to gently clean the bite area with mild soap and water as directed by your doctor.
- Dressing Changes: Change bandages as recommended by your healthcare provider, ensuring the wound remains protected.
- Avoid Soaking: Unless specifically advised by your doctor, avoid soaking the wound in water, as this can create a moist environment conducive to bacterial growth.
Managing Pain and Inflammation
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce fever. Follow dosage instructions carefully.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a clean, cold compress to the swollen area can help reduce inflammation and provide relief. Ensure the compress is wrapped in a cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
Rest and Nutrition
- Rest: Allow your body to focus its energy on fighting the infection by getting adequate rest.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your immune system and promotes healing.
Preventing Future Bites and Infections: Proactive Protection
Understanding how to treat an infected bite is crucial, but prevention is always the best medicine. Implementing proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk.
Pet Safety and Hygiene
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Ensure your pets are up-to-date on vaccinations and receive regular veterinary care.
- Supervise Interactions: Always supervise interactions between children and pets, especially with young children who may not understand how to handle animals gently.
- Prompt Wound Cleaning: If a pet bite occurs, clean the wound immediately and thoroughly.
Outdoor Awareness
- Insect Repellent: Use effective insect repellents when spending time outdoors, especially in areas known for mosquitoes, ticks, and other biting insects.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves and pants when hiking or in areas with tall grass to minimize exposure to ticks and other insects.
- Tick Checks: After spending time outdoors, perform thorough tick checks on yourself and your family, paying close attention to areas like the scalp, armpits, and groin.
General Hygiene Practices
- Handwashing: Frequent and thorough handwashing is a simple yet highly effective way to prevent the spread of germs.
- Avoid Provoking Animals: Never approach or provoke unfamiliar animals, whether wild or domestic.
Frequently Asked Questions About Infected Bites
Here are some common questions about how to treat an infected bite:
Q1: How quickly can a bite become infected?
A1: A bite can become infected within a few hours to a few days after the initial injury. Prompt cleaning and monitoring are essential.
Q2: What is the most common cause of infected bites?
A2: Bacteria from the mouth of the animal or human that caused the bite are the most common culprits.
Q3: Can I treat a spider bite at home if it looks infected?
A3: While minor insect bites can sometimes be managed at home, spider bites, especially those that show signs of infection or are from venomous species, should always be evaluated by a medical professional.
Q4: How long do I need to take antibiotics for an infected bite?
A4: The duration of antibiotic treatment will vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of antibiotic prescribed. It’s crucial to complete the full course as directed by your doctor.
Q5: What are the How to remove black pimples on face unveiling radiant skin long-term consequences of an untreated infected bite?
A5: Untreated infected bites can lead to serious complications, including cellulitis, abscesses, sepsis, tissue damage, and in rare cases, permanent disability or even death.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Your Health and Well-being
Navigating the complexities of how to treat an infected bite can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and prompt action, you can effectively manage and heal these common injuries. Remember, early detection, proper hygiene, and seeking professional medical advice when necessary are your most powerful tools. By understanding the signs, knowing when to act, and implementing preventative measures, you can ensure that a bite remains a minor inconvenience rather than a serious health concern. Stay vigilant, prioritize your well-being, and enjoy your activities with the confidence that you are prepared to handle any bite-related challenges.
Share this vital information with your friends and family to help them stay safe and healthy!




You may also like

How to Clear Pregnancy Acne: Your Radiant Glow Guide

How to Get Rid of Baby Pimples: A Gentle Guide to Clearer Skin

How to Help Acne During Pregnancy: Your Radiant Skin Guide
Recent Posts
- How to Clear Pregnancy Acne: Your Radiant Glow Guide
- How to Get Rid of Baby Pimples: A Gentle Guide to Clearer Skin
- How to Help Acne During Pregnancy: Your Radiant Skin Guide
- What is Good for Pimple Scars? Unveiling Radiant Skin!
- What Helps With Pimple Scars: Unveiling Your Path to Flawless Skin!
- How to Get Rid of Scarred Pimples: Unlocking Radiant Skin!
Leave a Reply