How to Treat Vaginal Bumps: Your Ultimate Guide to Relief and Understanding
Discovering unexpected bumps in the vaginal area can be a source of worry and discomfort. But fear not! This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to understand, manage, and effectively how to treat vaginal bumps, bringing you much-needed relief and peace of mind.
Understanding Vaginal Bumps: Causes and Common Types
Vaginal bumps are a common occurrence and can manifest in various forms, each with its own set of causes and potential treatments. It’s crucial to identify the type of bump you’re experiencing to determine the most effective approach to how to treat vaginal bumps.
Common Culprits Behind Vaginal Bumps
Several factors can contribute to the appearance of bumps in the vulvar and vaginal regions. Understanding these underlying causes is the first step towards finding the right solution.
1. Folliculitis: The Inflamed Hair Follicle
Folliculitis is a frequent cause of small, red bumps that can resemble pimples. It occurs when hair follicles become inflamed or infected, often due to bacteria.
- Causes: Shaving, waxing, tight clothing, friction, and poor hygiene can all contribute to folliculitis.
- Appearance: Small, red, sometimes pus-filled bumps, often itchy or tender. They can appear anywhere hair grows in the genital area.
- Treatment: For mild cases, warm compresses and gentle cleansing can help. Over-the-counter antibiotic creams may be recommended. Severe infections might require prescription medication.
2. Ingrown Hairs: The Unruly Guest
Ingrown hairs are another common offender, especially after hair removal. They happen when a hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin instead of emerging from the follicle.
- Causes: Shaving, waxing, and epilating are primary culprits.
- Appearance: Red, raised bumps that can sometimes have a visible hair trapped beneath the skin. They can be itchy and sore.
- Treatment: Gently exfoliating the area can help release trapped hairs. Avoid picking or squeezing, as this can lead to infection. Warm compresses can also soothe the area.
3. Bartholin’s Cysts: The Swollen Gland
Bartholin’s glands are located on either side of the vaginal opening and produce lubrication. Sometimes, these glands can become blocked, leading to a cyst.
- Causes: Blockage of the duct, often due to injury, infection, or inflammation.
- Appearance: A painless lump or swelling near the vaginal opening. If infected, it can become a painful abscess.
- Treatment: Small, painless cysts often resolve on their own. Warm sitz baths can help reduce swelling. If infected or causing significant discomfort, medical attention is necessary for drainage and antibiotics.
4. Genital Warts: The Viral Visitor
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Causes: Sexual contact with someone who has HPV.
- Appearance: Small, flesh-colored, cauliflower-like bumps or clusters. They can be itchy or cause discomfort.
- Treatment: Genital warts require medical diagnosis and treatment. Options include topical medications, cryotherapy (freezing), or surgical removal. Condom use can help prevent transmission.
5. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): The Recurring Outbreak
Genital herpes is an STI caused by HSV, which can cause recurring outbreaks of sores or blisters.
- Causes: Sexual contact with someone who has HSV.
- Appearance: Clusters of small, painful blisters that can break open and form sores. Flu-like symptoms may accompany the first outbreak.
- Treatment: While there is no cure for herpes, antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks, reduce their severity and duration, and lower the risk of transmission.
6. Molluscum Contagiosum: The Pearly Pustules
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes small, pearly or flesh-colored bumps with a dimple in the center.
- Causes: Direct skin-to-skin contact, often through sexual contact or sharing personal items.
- Appearance: Small, raised, dome-shaped bumps, usually painless.
- Treatment: Molluscum contagiosum often resolves on its own over time. However, for cosmetic reasons or to prevent spread, a doctor may recommend cryotherapy, topical treatments, or curettage (scraping).
7. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Beyond Warts and Herpes
Other STIs can also present with bumps or lesions in the genital area.
- Syphilis: Can cause a painless sore called a chancre, which may appear as a firm, round bump.
- Chancroid: Causes painful open sores with irregular borders.
- Treatment: Prompt medical diagnosis and treatment are crucial for all STIs. Antibiotics are typically prescribed.
8. Skin Tags: The Benign Growths
Skin tags are small, soft, benign growths that can appear in various parts of the body, including the genital area.
- Causes: Often associated with friction, hormonal changes, or genetics.
- Appearance: Small, soft, flesh-colored flaps of skin. They are usually painless.
- Treatment: Skin tags are generally harmless and do not require treatment. If they cause irritation or are a cosmetic concern, a doctor can remove them through freezing, cutting, or burning.
9. Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS): The Chronic Condition
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects hair follicles, often in areas with sweat glands, including the groin.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but it involves a blockage of hair follicles and inflammation.
- Appearance: Painful lumps, boils, and abscesses that can lead to scarring.
- Treatment: HS is a chronic condition requiring ongoing management. Treatment options include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, hormonal therapies, and sometimes surgery.
When to Seek Medical Advice: Recognizing Red Flags
While many vaginal bumps are benign and can be managed at home, it’s essential to know when to consult a healthcare Pimple inside my cheek a frustrating yet manageable oral annoyance professional. Prompt medical attention ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, especially for potential STIs or more serious conditions.
Signs That Warrant a Doctor’s Visit
- Sudden onset of severe pain or swelling.
- Bumps that are rapidly growing or changing in appearance.
- Fever or other signs of systemic infection.
- Bumps that are accompanied by unusual discharge or odor.
- Any suspicion of a sexually transmitted infection.
- Bumps that persist for more than a few weeks despite home care.
- Recurrent or worsening symptoms.
A healthcare provider can perform a physical examination, ask about your medical history, and may recommend diagnostic tests such as swabs or blood work to determine the cause of the bumps and guide the best course of action for how to treat vaginal bumps.
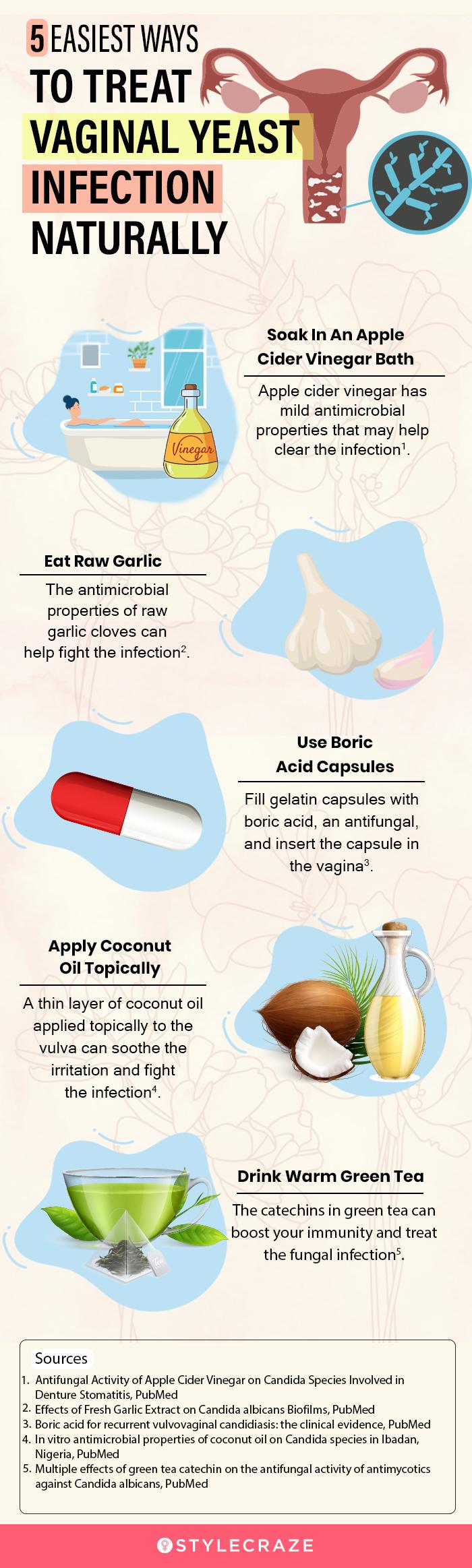
Effective Strategies for How to Treat Vaginal Bumps at Home
For minor bumps and irritations, several home remedies and self-care practices can provide relief and promote healing. Remember, these are best suited for conditions like folliculitis or ingrown hairs.
Gentle Cleansing and Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene is paramount.
- Use mild, unscented soaps: Harsh chemicals can irritate sensitive skin. Opt for gentle, hypoallergenic cleansers.
- Wash regularly: Cleanse the genital area daily with warm water and a mild soap.
- Pat dry gently: Avoid vigorous rubbing, which can cause irritation.
Warm Compresses: A Soothing Solution
Warm compresses can help reduce inflammation, pain, and promote drainage for certain types of bumps.
- How to apply: Soak a clean cloth in warm (not hot) water, wring out the excess, and gently hold it against the affected area for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
Exfoliation: Releasing Trapped Hairs
For ingrown hairs, gentle exfoliation can be beneficial.
- Use a soft washcloth or a gentle exfoliating scrub: Be very careful not to irritate the skin further.
- Avoid harsh scrubbing: This can worsen inflammation.
Loose-Fitting Clothing: Allowing the Skin to Breathe
Tight clothing can trap moisture and heat, exacerbating irritation and promoting bacterial growth.
- Opt for breathable fabrics: Cotton underwear is ideal.
- Avoid tight jeans, leggings, or synthetic materials: Especially when experiencing bumps.
Over-the-Counter Treatments (Use with Caution)
For mild folliculitis or irritation, some over-the-counter options might offer relief.
- Antibiotic ointments: For minor bacterial infections, an over-the-counter antibiotic cream can be helpful. Always follow product instructions.
- Hydrocortisone cream: A low-dose hydrocortisone cream can help reduce itching and inflammation for non-infectious bumps. Use sparingly and as directed.
Important Note: Always consult a pharmacist or doctor before using any over-the-counter medication, especially in the sensitive genital area.
Medical Treatments for Persistent or Severe Vaginal Bumps
When home remedies aren’t sufficient or when a medical condition is diagnosed, your doctor will recommend specific treatments.
Prescription Medications
- Topical Antibiotics: For more significant bacterial infections.
- Oral Antibiotics: For widespread or severe infections.
- Antiviral Medications: For herpes outbreaks, to manage symptoms and reduce transmission.
- Topical Steroids: For severe inflammation and itching.
Procedures
- Incision and Drainage: For infected Bartholin’s cysts or abscesses.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing off genital warts.
- Laser Therapy: Another option for treating genital warts.
- Surgical Excision: For large or persistent skin tags or other benign growths.
Prevention: Minimizing Your Risk of Vaginal Bumps
The best approach to managing vaginal bumps is often prevention. By adopting healthy habits, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing them.
Smart Hair Removal Practices
- Shave in the direction of hair growth: This minimizes irritation and the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Use a sharp, clean razor: Dull blades can cause nicks and irritation.
- Consider alternatives to shaving: Waxing, epilating, or laser hair removal can reduce the frequency of ingrown hairs for some individuals.
- Moisturize after hair removal: This helps keep the skin hydrated and can prevent ingrown hairs.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
- Wash the genital area daily: Use a mild, unscented soap and warm water.
- Avoid douching: Douching disrupts the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, making it more susceptible to infections.
- Change tampons and pads regularly: During menstruation.
Wearing Breathable Underwear
- Choose cotton underwear: It allows for better air circulation than synthetic materials.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing: Especially during hot or humid weather.
Practicing Safe Sex
- Use condoms: Condoms are crucial for preventing the transmission of STIs that can cause genital bumps.
- Get regular STI screenings: If you are sexually active, regular testing is important for early detection and treatment.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
- Diabetes: If you have diabetes, maintaining good blood sugar control can help prevent skin infections.
- Obesity: For conditions like hidradenitis suppurativa, weight management can sometimes help.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vaginal Bumps
Here are answers to some common questions regarding vaginal bumps:
Q1: Are vaginal bumps always a sign of an STI?
A1: No, not at all! While some vaginal bumps can be caused by STIs like genital warts or herpes, many are due to benign causes like folliculitis, ingrown hairs, or Bartholin’s cysts. It’s important not to jump to conclusions and to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis.
Q2: Can I pop a vaginal bump like a pimple?
A2: It is strongly advised not to pop or squeeze vaginal bumps. This can worsen inflammation, spread infection, and lead to scarring. It’s best to let them heal naturally or seek medical treatment.
Q3: How long does it take for vaginal bumps to go away?
A3: The healing time varies greatly depending on the cause. Mild folliculitis or ingrown hairs might resolve within a few days to a week with proper care. Bartholin’s cysts can take longer, and STIs require medical treatment for resolution.
Q4: Can stress cause vaginal bumps?
A4: While stress doesn’t directly cause most vaginal bumps, it can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections that can lead to bumps. Stress can also exacerbate existing skin conditions.
Q5: What is the best way to treat an itchy vaginal bump?
A5: For itchy bumps, focus on gentle cleansing and avoiding scratching. Applying a cool compress can provide relief. If the itch is severe or persistent, consult a doctor, as it might indicate an infection or an allergic reaction.
Embrace Confidence and Comfort: Your Journey to Health
Understanding how to treat vaginal bumps is about empowering yourself with knowledge and taking proactive steps towards your well-being. Remember, you are not alone in experiencing these concerns. By staying informed, practicing good hygiene, and seeking professional medical advice when needed, you can effectively manage and overcome any vaginal bumps, ensuring comfort and confidence in your intimate health. Don’t let these minor inconveniences dim your sparkle!
Share your experiences or any tips you’ve found helpful in the comments below! Let’s support each other on our journey to optimal vaginal health.







You may also like

How to Clear Pregnancy Acne: Your Radiant Glow Guide

How to Get Rid of Baby Pimples: A Gentle Guide to Clearer Skin

How to Help Acne During Pregnancy: Your Radiant Skin Guide
Recent Posts
- How to Clear Pregnancy Acne: Your Radiant Glow Guide
- How to Get Rid of Baby Pimples: A Gentle Guide to Clearer Skin
- How to Help Acne During Pregnancy: Your Radiant Skin Guide
- What is Good for Pimple Scars? Unveiling Radiant Skin!
- What Helps With Pimple Scars: Unveiling Your Path to Flawless Skin!
- How to Get Rid of Scarred Pimples: Unlocking Radiant Skin!
Leave a Reply